A simple explanation of var let and const in JavaScript

What is var?
In JavaScript, var is a keyword used to declare variables. Variables declared with var are function-scoped, meaning they can be accessed anywhere within the function they were declared in. If a variable is declared with var outside of a function, it becomes a global variable and can be accessed anywhere in the code.
One thing to be aware of when using var is hoisting. var declarations are hoisted to the top of their scope, meaning that even if a var declaration appears later in the code, it will still be treated as if it was declared at the beginning of the scope. This can lead to unexpected behavior and bugs.
While var is still supported in modern JavaScript, it has largely been replaced by let and const, which have more predictable scoping behavior.
var userName = "Shrish"
function greet(name) {
console.log("Good Morning" + name)
}
greet(userName) // Output Good Morning Shrish
What is let?
In JavaScript, let is a keyword used to declare variables. Variables declared with let are block-scoped, meaning they are only accessible within the block of code they were declared in, such as within a function, loop, or conditional statement. Unlike var, let declarations are not hoisted to the top of their scope, so they can only be accessed after they have been declared.
One benefit of using let over var is that it can help prevent bugs and unintended behavior caused by global variables. let also allows for variable reassignment, meaning you can change the value of a let variable throughout the code. Overall, let provides a more predictable scoping behavior and can help make code easier to read and maintain.
let userName = "Max"
function greet(name) {
let name = "Manu"
console.log("Hello " + name)
}
greet(userName) // Hello Manu because of the block scope of let
What is const?
In JavaScript, the const keyword is used to declare variables that cannot be reassigned to a different value after their initial assignment. This can be useful for defining variables that should remain constant throughout a program's execution, such as configuration settings or mathematical constants. However, it is important to note that const does not make the variable immutable, meaning its properties or elements can still be modified.
Also, unlike let or var, a const variable must be assigned a value when declared. Additionally, const variables have block scope, meaning they are only accessible within the block they were defined in.
Scopes in var let and const
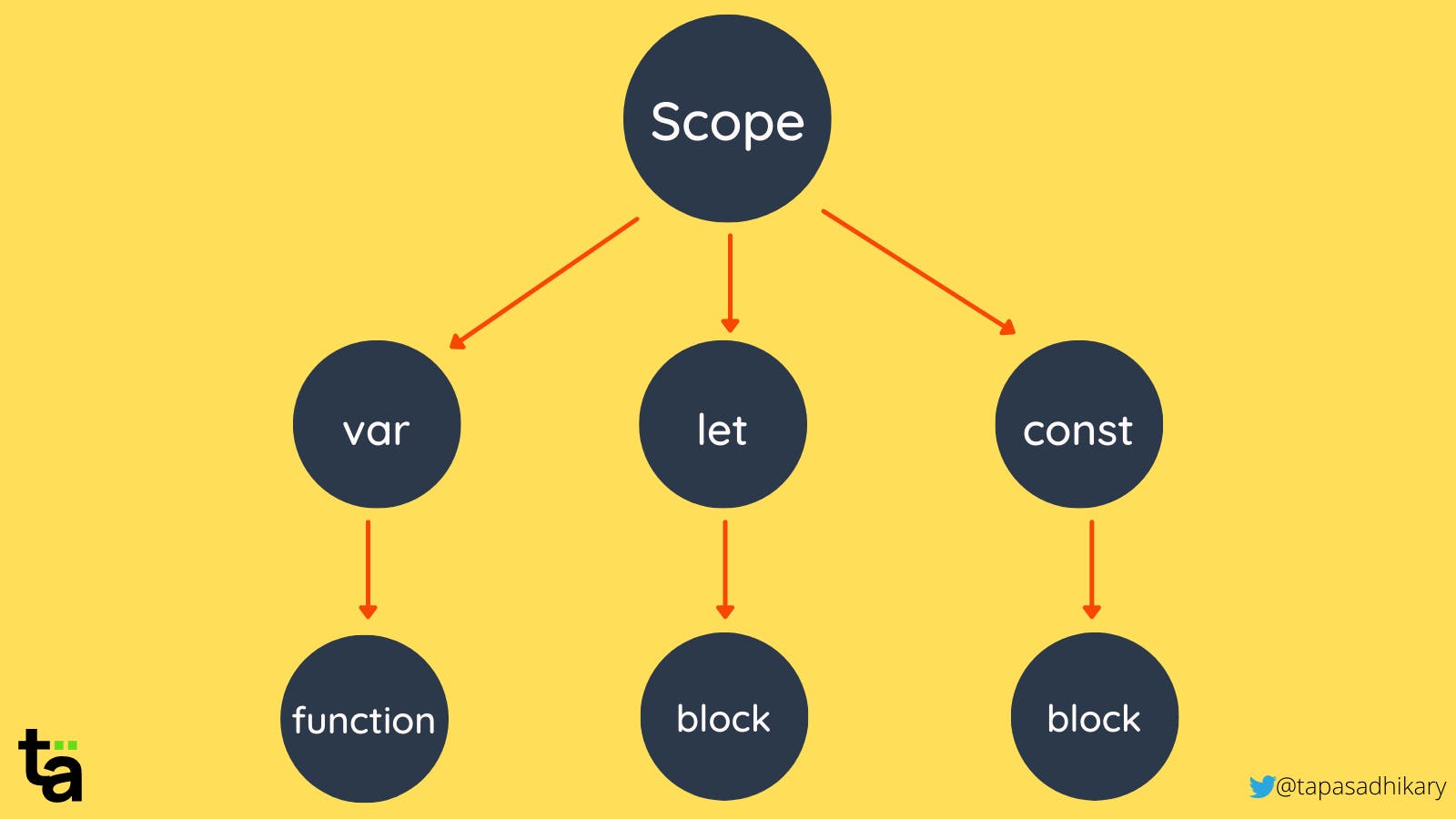
varis a keyword used for declaring variables in JavaScript. It has function scope, meaning that variables declared withvarare accessible anywhere within the in which they are declared. However, if avarvariable is declared outside of anyfunction, it becomes globally scoped and is accessible anywhere in the code.letandconstare keywords introduced in ECMAScript 6 and they have block scope, meaning that they are only accessible within the block in which they are declared. A block is defined by a pair of curly braces({...})and can be aloop, orconditionalstatement.letallows the variable to be reassigned, whereasconstdeclares a variable that cannot be reassigned after its initial assignment. However, it's important to note thatconstonly makes the variable itself immutable, not its properties or if it is anobjectorarray.In summary,
varhasfunctionscope and can be hoisted,letandconsthave block scope and are not hoisted.letallows reassignment whileconstdoes not.
Some differences between var, let, and const
| Type | var | let | const |
| Scope | function scope | block scope | block scope |
| Hoisted | Yes | No | No |
| Reassign | Yes | Yes | No |
| Redeclare | Yes | No | No |
| Global Scope | Yes | No | No |
